Postal Index Number
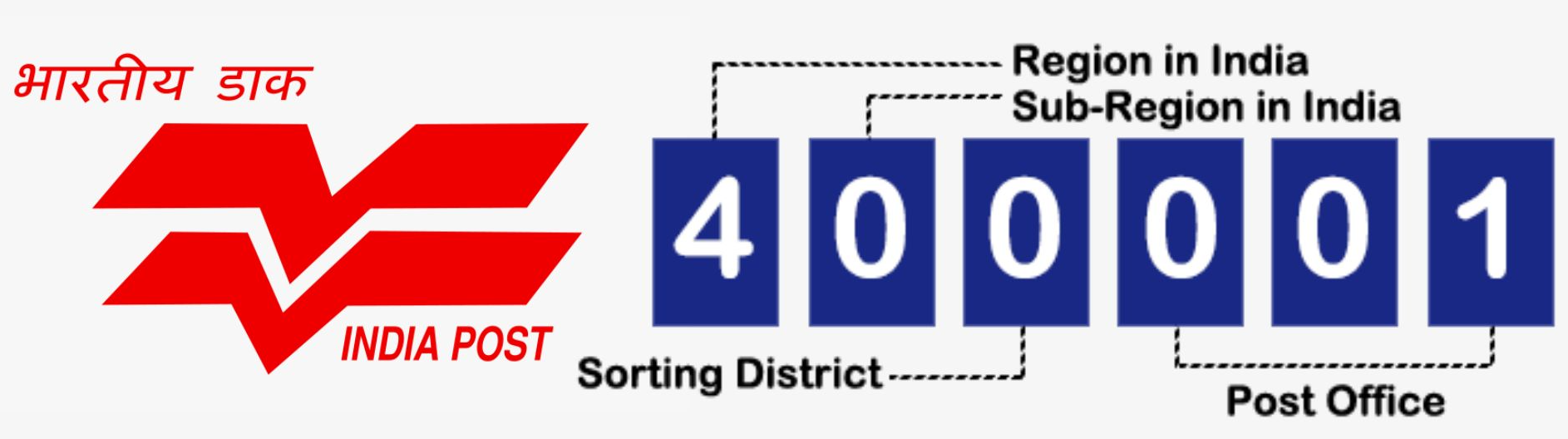
An Indian PIN code (Postal Index Number) is a six-digit numerical code used by the Indian postal system to identify specific geographic locations for efficient mail delivery. The PIN was introduced on August 15, 1972. There are 9 PIN regions in the country. The first 8 are geographical regions and the digit 9 is reserved for the Army Postal Service. The first digit indicates one of the regions. The first 2 digits together indicate the sub region or one of the postal circles. The first 3 digits together indicate a sorting / revenue district. The last 3 digits refer to the delivery Post Office.
For example, a PIN code like 110001 corresponds to Connaught Place in New Delhi.
The first digit of a PIN code signifies the following:
| First Digit | Region | States Covered |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Northern | Delhi, Haryana, Punjab, Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir |
| 2 | Northern | Uttar Pradesh and Uttaranchal |
| 3 | Western | Rajasthan and Gujarat |
| 4 | Western | Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh |
| 5 | Southern | Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka |
| 6 | Southern | Kerala and Tamil Nadu |
| 7 | Eastern | West Bengal, Orissa and North Eastern |
| 8 | Eastern | Bihar and Jharkhand |
| 9 | APS | Army Postal Service |
The first two digit of a PIN code signifies the following:
| First 2 Digits of PIN | Circle |
|---|---|
| 11 | Delhi |
| 12 and 13 | Haryana |
| 14 to 16 | Punjab |
| 17 | Himachal Pradesh |
| 18 to 19 | Jammu & Kashmir |
| 20 to 28 | Uttar Pradesh and Uttaranchal |
| 30 to 34 | Rajasthan |
| 36 to 39 | Gujarat |
| 40 to 44 | Maharashtra |
| 45 to 49 | Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh |
| 50 to 53 | Andhra Pradesh |
| 56 to 59 | Karnataka |
| 60 to 64 | Tamil Nadu |
| 67 to 69 | Kerala |
| 70 to 74 | West Bengal |
| 75 to 77 | Orissa |
| 78 | Assam |
| 79 | North Eastern |
| 80 to 85 | Bihar and Jharkhand |
| 90 to 99 | Army Postal Service (APS) |